
For a beginning programmer, it is more important to understand the general attributes of the integer data type that apply to most programming languages. These variations of the integer data type are an annoyance for a beginning programmer. This effect is known as being machine dependent. The integer data type has similar attributes and acts or behaves similarly in all programming languages that support it. Third, integer processing is significantly faster within the CPU than is floating point processing. Second, the integer data type is often used to control program flow by counting, thus the need for a data type that jumps from one value to another. A dog, even with only 3 legs, is still one (1) dog not ¾ of a dog. First, some things in the real world are not fractional. It could be asked why not make all your numbers floating point which allow for fractional parts. The integer values jump from one value to another. The integer data type basically represents whole numbers (no fractional parts). The size of the grouping varies so the set of integer sizes available varies between different types of computers and different programming languages. Integers are commonly represented in a computer as a group of binary digits (bits). Integral data types may be of different sizes and may or may not be allowed to contain negative values. For example, a memory allocation function void *malloc( size_t size ) returns a pointer to void which can be casted to any data type.An integer data type represents some range of mathematical integers. For example, int rand(void) Ī pointer of type void * represents the address of an object, but not its type.
A function with no parameter can accept a void. There are various functions in C which do not accept any parameter. A function with no return value has the return type as void. There are various functions in C which do not return any value or you can say they return void. It is used in three kinds of situations − Sr.No. The void type specifies that no value is available. Printf("Precision value: %d\n", FLT_DIG ) Printf("-DBL_MAX : %g\n", (double) -DBL_MAX) Printf("DBL_MIN : %g\n", (double) DBL_MIN) Printf("DBL_MAX : %g\n", (double) DBL_MAX) Printf("-FLT_MIN : %g\n", (float) -FLT_MIN) Printf("-FLT_MAX : %g\n", (float) -FLT_MAX) Printf("FLT_MIN : %g\n", (float) FLT_MIN) Printf("FLT_MAX : %g\n", (float) FLT_MAX) Printf("Storage size for float : %d \n", sizeof(float)) The following example prints the storage space taken by a float type and its range values − The header file float.h defines macros that allow you to use these values and other details about the binary representation of real numbers in your programs. The following table provide the details of standard floating-point types with storage sizes and value ranges and their precision − Type When you compile and execute the above program, it produces the following result on Linux − Printf("USHRT_MAX : %d\n", (unsigned short) USHRT_MAX) Printf("ULONG_MAX : %lu\n", (unsigned long) ULONG_MAX)

Printf("UINT_MAX : %u\n", (unsigned int) UINT_MAX)
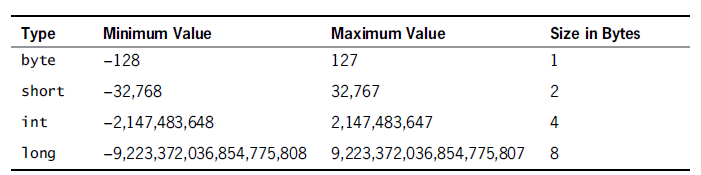
Printf("LONG_MIN : %ld\n", (long) LONG_MIN) Printf("LONG_MAX : %ld\n", (long) LONG_MAX) Given below is an example to get the size of various type on a machine using different constant defined in limits.h header file − The expressions sizeof(type) yields the storage size of the object or type in bytes. To get the exact size of a type or a variable on a particular platform, you can use the sizeof operator. The following table provides the details of standard integer types with their storage sizes and value ranges − Type We will see the basic types in the following section, where as other types will be covered in the upcoming chapters. The type of a function specifies the type of the function's return value. The array types and structure types are referred collectively as the aggregate types. They include (a) Pointer types, (b) Array types, (c) Structure types, (d) Union types and (e) Function types. The type specifier void indicates that no value is available. They are again arithmetic types and they are used to define variables that can only assign certain discrete integer values throughout the program. They are arithmetic types and are further classified into: (a) integer types and (b) floating-point types. The types in C can be classified as follows − Sr.No. The type of a variable determines how much space it occupies in storage and how the bit pattern stored is interpreted. Data types in c refer to an extensive system used for declaring variables or functions of different types.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
